RFID from the ground up - what is the technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a contactless radio frequency identification technology that enables fast and accurate recognition of objects. Although it is not new – the first attempts to use radio waves to identify aircraft took place as early as World War II – today RFID is returning to favor as a key component of modern automatic identification and warehouse logistics systems.
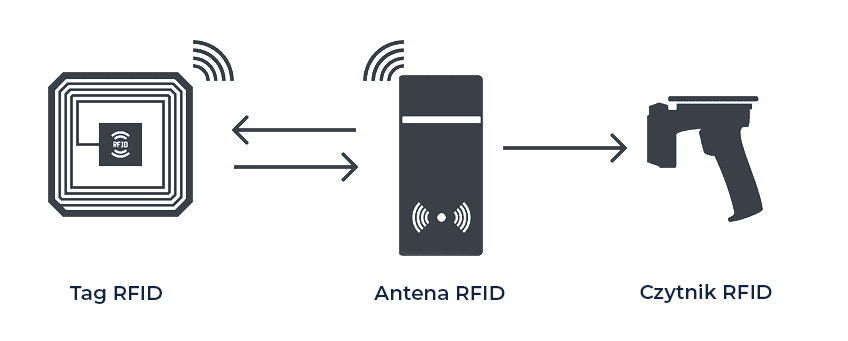
RFID system consists of three basic components:
RFID reader,
identification chip (tag),
The computer system that controls the readings.
An RFID reader emits radio waves that activate a chip embedded in a label or durable medium, such as an identification tag or lozenge. The data stored in the chip is then read and transmitted to the system. It is the system that is responsible for the reading logic – initiating specific actions or generating reports based on the acquired data.
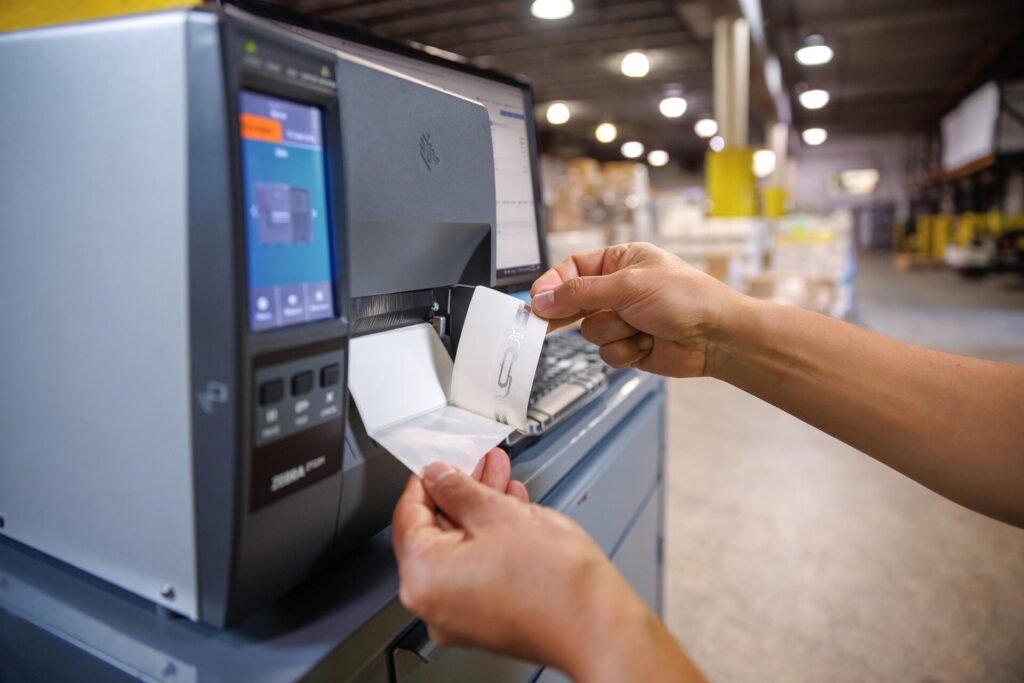

RFID vs barcodes - key differences
RFID technology is sometimes seen as an alternative to barcodes, although in practice it more often complements them. This is primarily due to cost – RFID labels are many times more expensive than traditional barcode labels, which limits their mass application.
Nevertheless, RFID offers a number of technological advantages:
Reading without physical contact with the product,
The ability to read multiple tags simultaneously,
Reading range of up to 5 meters (for UHF technology).
Thanks to these properties, RFID makes it possible to significantly speed up logistics processes and improve their accuracy.
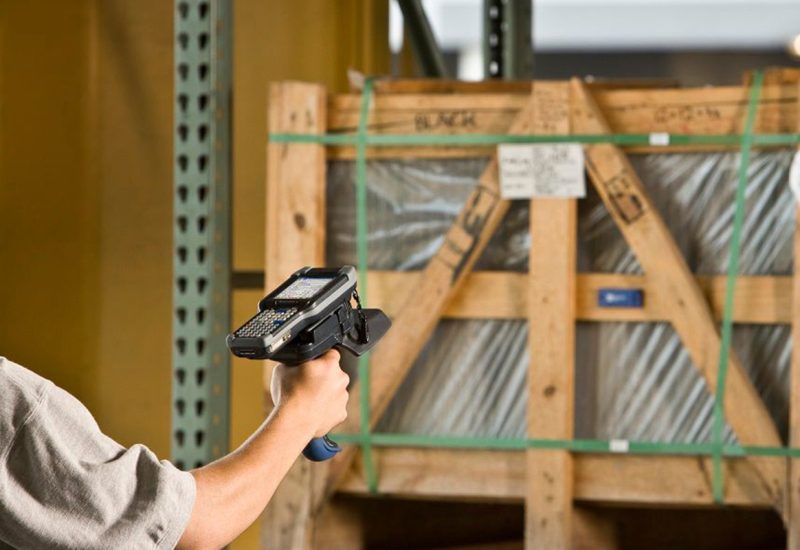

Where is RFID worth applying?
RFID is used wherever speed, precision and control of assets are crucial. The technology is ideal for:
High-value products such as clothing, jewelry or electronics,
inventory of fixed assets Without the need for physical contact with the items,
management of reusable packaging,
Monitoring production processes – especially in the automotive industry,
marking of outdoor facilities and infrastructure.
RFID is increasingly becoming an integral part of modern WMS and warehouse automation, supporting the development of the concept of digital twin and comprehensive automatic identification (Auto ID).
RFID does not replace barcodes, but complements them perfectly, offering a whole new level of automation and control. Today, with component prices falling and IT infrastructure maturing, the technology has a chance to finally deliver on its original promises - realistically supporting logistics, production and asset management.




